Towards giving lectures - class review
Last updated on:3 years ago
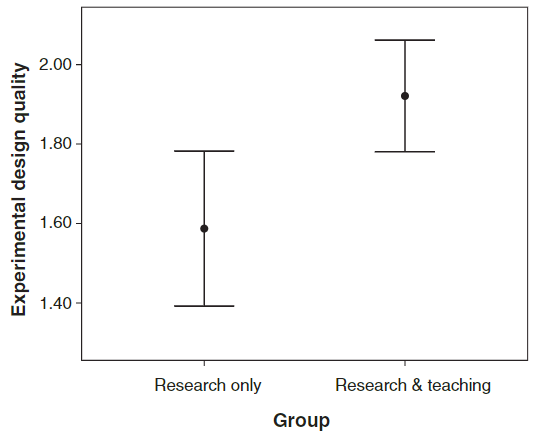
Teaching is one of my favourite things and hobbies. Luckily, I have a chance to learn the fundamental theories about teaching students. Teaching experience can contribute substantially to the improvement of essential research skills.
ILOs, intended learning outcomes
- Describe the context for learning and teaching at CityU.
- Apply outcomes-based teaching and learning (OBTL).
- Approach to student learning.
- Utilize eLearning tools in education.
- Deliver high-quality instruction and learning activities.
What will the learners be able to do when they have completed their course or programme?
Expressed from the students’ perspective.
Expressed in the form of action verbs leading to observable and assessable behaviour.
Related to criteria.
Ideally, no more than three/five outcomes per session/course
Outcomes should be achievable and assessable.
TLA, teaching and learning activities
These are simply activity that stimulates, encourages or facilitates learning of one or more intended learning outcomes.
They ensure that the TLA is appropriate for the ILO and any subsequent assessment tasks are essential. They can be as diverse as lectures, role play, internships, exchanges and discussions. Can use a particular learning theory to guide the development of the activity - operant learning, social-cognitive, constructivist, etc.

Assessment tasks
Before designing any assessment tasks, an essential first step is to decide what performances would represent evidence that a particular learning outcome has been achieved.
A second step is to ensure an alignment between the learning outcome and the evidence.
The key to achieving alignment mainly rests with the action verbs we choose, identifying what a learner can do after successfully completing the Teaching and Learning Activity.
Student performance in assessment tasks should be judged against a set of clear assessment criteria defining the quality of performance expected of each of grade.
An alignment:

EMI, medium of instruction
What do we need to know to help our students learn in English?
- Context: fluency/accuracy & learner language
- Challenges faced by university students in Hong Kong
- Measures we can take to help address those challenges
Assessment
What is the purpose of assessment?
From teachers‘ perspectives:
- Making judgements on student performance
- Evaluating the effectiveness of a course (informing how teachers teach)
- Being part of the teaching and learning activities
- From students‘ perspectives:
Motivating students to learn (being part of the learning experience)
- Demonstrating skills and knowledge learned
- Receiving feedback on their performance
- Acquiring academic qualifications
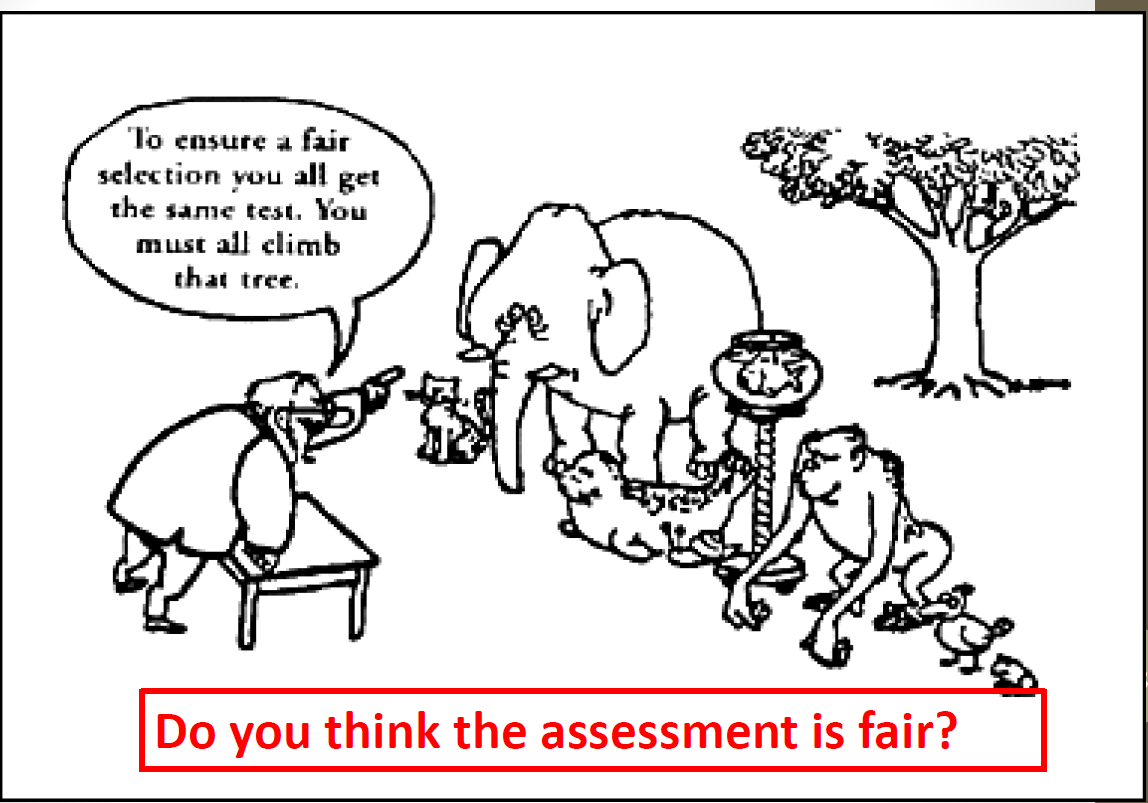

The picture is intriguing but misleading. I think there are chances for any student to choose some proper course with proper difficulties for them. However, once they choose the same course, we should not open a back door for the minority of them. But don’t worry, if they can not fit for the course, they can work for something else.
The characteristics of effective assessment: Valid, reliable, consistent, transparent, fair, efficient and manageable, effective feedback.

Rubric
A rubric is a scoring guide that seeks to evaluate a student’s performance based on the sum of a full range of criteria.
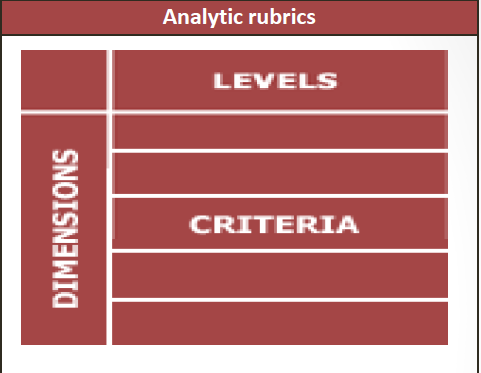
- A criterion is written for each dimension at each level
- Performance is assessed along separate dimensions; the grade is decided by adding the scores of the parts
- Different weighting may be allocated to each dimension to account for their relative importance
Feedback
Function:
- To sum up the final judgment of the quality of the students’ work
- To help students improve their work in future
Characteristics:
Informative, criterion-referenced, motivating, timely
Engaging your audiences
Eye contact
- Voice (speak loud and clear)
- Body language
- Gestures
- Enthusiasm (passion)
- Friendliness
Voice
- Rate of speech
- Volume
- Pitch or tone
- Articulation/pronunciation
- Emphasis
- Vocalized pauses
Podium panic, feeling nervous?
- Lack of experience
- Lack of preparation
- Lack of enthusiasm
Practical tips
- Rehearse the lesson
- Practice
- Beginning the presentation with a slow, well-prepared introduction
Approaches
- Introducing/motivating by a question, story, quote, video, etc.
- Showing and telling with examples, facts, figures
- Interactive, teaching and learning activities
Reference
[1] Feldon, D.F., Peugh, J., Timmerman, B.E., Maher, M.A., Hurst, M., Strickland, D., Gilmore, J.A. and Stiegelmeyer, C., 2011. Graduate students’ teaching experiences improve their methodological research skills. Science, 333(6045), pp.1037-1039.
[2] CityU, SG8001S02 Teaching Students: First Steps.
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!