Cell Biology -- Review Notes
Last updated on:4 months ago
I acquired a foundation in biology during my junior and senior years of high school, where I excelled compared to my peers. However, much of what I learned back then has faded from my memory. I am considering joining a biomedical engineering lab as a PhD candidate. Before I do, I aim to refresh my knowledge by writing a review of cell biology. To aid in reading English scientific papers, I have also translated some of the technical terms into Chinese.
Cell biology
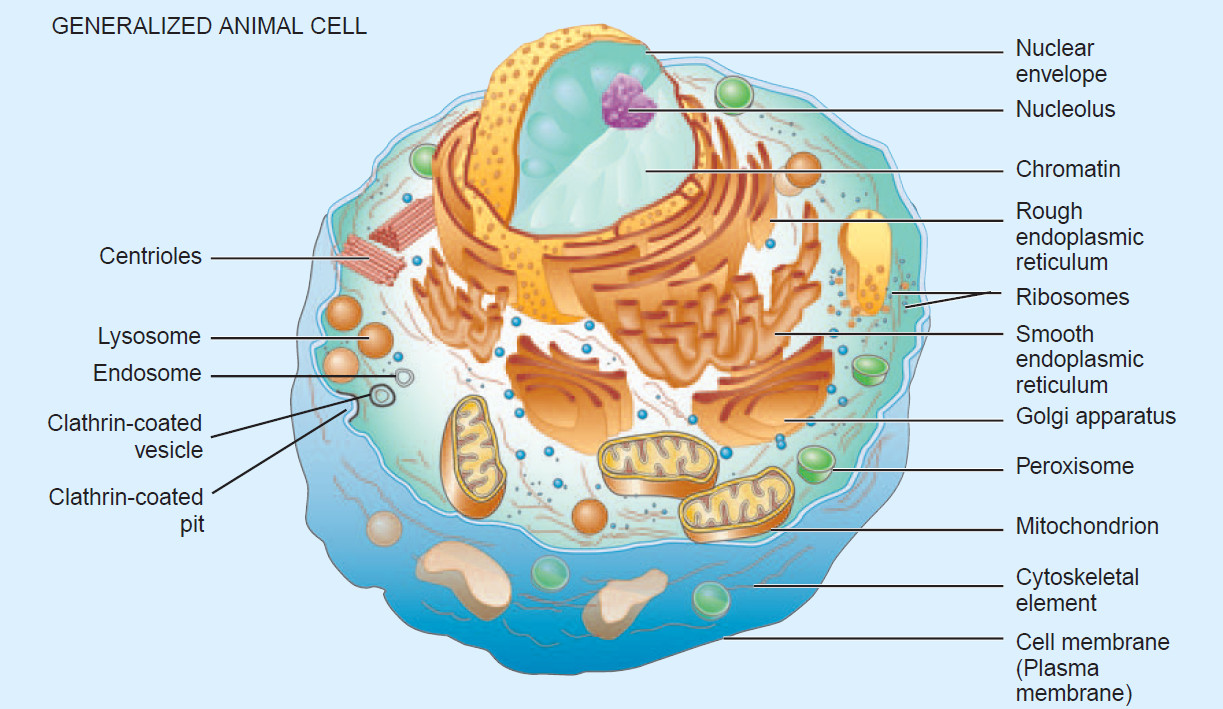
- Nuclear envelop (细胞核膜),
- Chromatin (染色质): Chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (粗糙内质网): This is a network of membranous tubules within the cytoplasm of a cell, studded with ribosomes involved in protein synthesis.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (光滑内质网): Unlike the rough ER, the smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid manufacture and metabolism, as well as detoxification.
- Golgi Apparatus (高基体): An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for storage or transport out of the cell.
- Peroxisome (过氧化物酶体): An organelle containing enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, creating hydrogen peroxide as a by-product.
- Mitochondrion (线粒体): Known as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria generate most of the cell’s supply of ATP, which is used as a source of chemical energy.
- Cytoskeletal Element (细胞骨架元素): The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement.
- Clathrin-coated Pit (克拉思林包裹的凹陷): Specialized sites on the cell membrane that play a major role in the formation of vesicles for endocytosis.
- Clathrin-coated Vesicle (克拉思林包裹的囊泡): These vesicles transport molecules to different parts within the cell, particularly from the plasma membrane and the trans-Golgi network.
- Endosome (内体): Membrane-bound compartments in the cell that sort the ingested material and recycle back to the cell surface.
- Lysosome (溶酶体): An organelle containing digestive enzymes capable of breaking down many types of biomolecules.
- Centrioles (中心体): A small set of microtubules arranged in a specific way, involved in cellular division and cellular structure.
Multi-omics data
- Metabolism: encompasses all the chemical reactions that occur within an organism to maintain life.
Reference
[1] Goodman, S.R. ed., 2007. Medical cell biology. Academic Press.
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!